Know About Incontinence
Overview
- If you are unseaworthy excretory product after you cough, laugh or sneeze, otherwise you have unforeseen urges to travel to the lavatory that square measure therefore intense you worry you will not get there in time, you’re probably experiencing incontinence. The inability to control urination is frequently a treatable, and often curable, problem faced by millions of Americans, many of them women.
While at least half the elderly experience the condition, and it is a major cause of admission to nursing homes, it is often mistakenly thought of as a problem suffered only by older people. In fact, incontinence can occur at any age.
Although the bulk of incontinence cases is improved or cured, several of these afflicted ne’er discuss their drawback with a health care skilled. Instead of recognizing incontinence as a treatable condition and following treatment, many ladies read it as AN embarrassing consequence of aging. They may wear absorbent product and don’t ask for treatment. Health care professionals may recommend using absorbent products during treatment or as part of treatment, but rarely as the only treatment for incontinence.Left untreated, incontinence can lead to skin rashes and infections, loss of self-esteem, emotional distress and self-imposed isolation. You don’t need to suffer incontinence in silence, as there square measure many treatment choices from that you and your health care skilled will opt for.
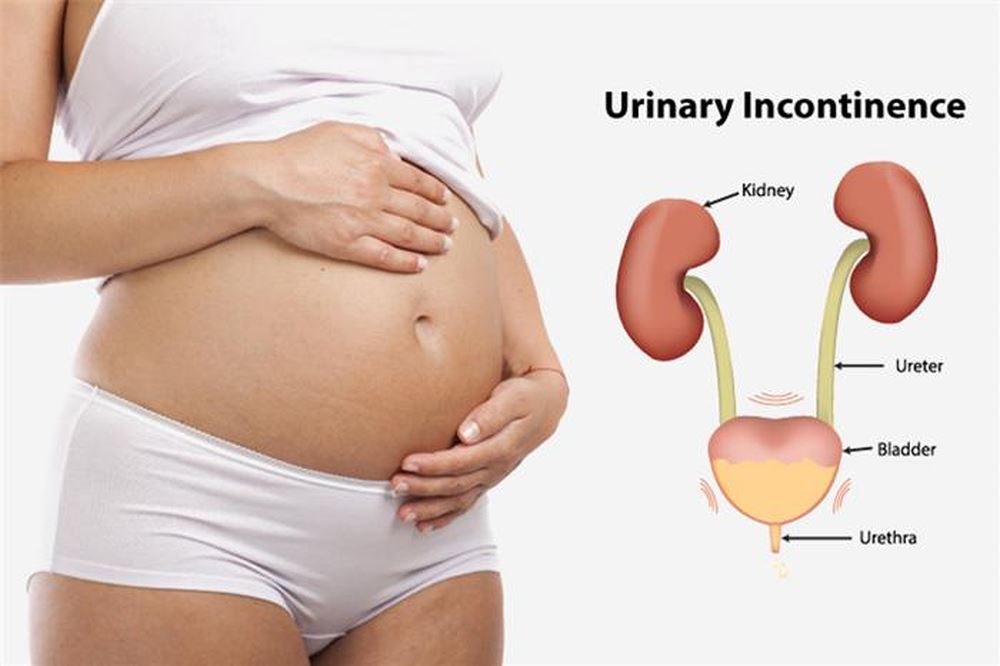
Incontinence isn’t a disease—it’s a symbol which will be caused by a large vary of conditions, like weak girdle floor muscles from previous vaginal birth or AN active bladder muscle from aging. Less oft, diabetes, stroke and nerve diseases, likemultiple sclerosis, may also cause leakage. Your tract includes 2 kidneys, 2 ureters, the bladder and therefore the channel. Your kidneys take away waste and water from your blood to provide excretory product. Urine travels through muscular tubes known as the ureters to the bladder. The bladder could be a balloon-like organ composed of muscle, animal tissue and nerves that expands because it fills with excretory product. Urine is stored in the bladder until it is released from the body through a tube called the urethra.
Circular muscles, called the urinary sphincters, control the activity of the urethra. The sphincter muscles prevent the loss of urine. The sphincters close off the base of the bladder—like a rubber band at the base of a balloon—so you do not leak urine.
As the bladder fills with urine, you have an increasing urge to urinate. Sensory nerves in the bladder signal your brain when the bladder is full. Just before you urinate, the sphincter first relaxes and then, in reflex fashion the bladder muscle contracts, squeezing urine out through the urethra. When you stop urinating, the bladder muscle relaxes, and the sphincters contract.Incontinence will worsen due to aging, illness or injury. A urinary tract infection, vaginal infection or irritation and constipation may result in temporary bouts of incontinence that are alleviated by treating the primary ailment. Additionally, some medications can cause incontinence, and changing or discontinuing a drug may bring relief. Women United Nations agency square measure pregnant may additionally suffer from temporary bladder management issues, which are caused by hormonal changes and pressure exerted on the urinary tract by the growing fetus.
Most incontinence in girls is triggered by issues with the bladder and anatomical sphincter muscles, which can weaken with age. A bladder muscle that’s too active, weak pelvic muscles resulting from pregnancy and childbirth, hormonal imbalances in menopausal women, nerve disorders and immobility also can contribute to incontinence. Although these bladder management issues tend to be long-run, many women who seek treatment see an improvement or are cured.
To help you higher perceive your incontinence and higher justify it to your health care skilled, it’s useful to acknowledge what reasonably incontinence you will have. Health care professionals classify incontinence by the symptoms displayed or the circumstances occurring at the time urine is involuntarily released. The following are types of urinary incontinence:
orm of incontinence in women. This occurs when any kind of pressure is put on the bladder, such as during sneezing, laughing, lifting, running, coughing, exercising, walking or even rising from a chair. Childbirth and weight gain are two common causes of incontinence because these conditions stretch the pelvic floor muscles. The pelvic floor muscles support the bladder, and when they are stretched, the neck of the bladder, or the place where the bladder and the urethra meet, drops and pushes against the vagina wall, preventing the sphincter muscles that force the urethra shut from tightening as well as they should. The result is urine leaks during physical stress. Stress incontinence also can occur when the sphincter muscles themselves weaken. Additionally, decreased estrogen levels may cause the lining of the urethra to thin, reducing bladder support.
- Urge incontinence is characterized by urgent needs to urinate, followed by sudden urine leakage. Occasionally, some women have no warning or urge sensation. You also may leak urine when you drink small amounts of liquid, or when you hear or touch running water. You may go to the bathroom as often as every two hours, and you may wet the bed at night or wake multiple times during the night to urinate. Involuntary bladder contractions are the most common cause of urge incontinenceand are described by health care professionals as “overactive,” “unstable” or “spastic” bladder. It is often difficult to assign a direct cause to the involuntary bladder muscle contractions. In rare instances, these can be caused by damage to the bladder muscle or nerves, or to the body’s nervous system, including the spinal cord and brain. Such damage may be caused by diseases such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, stroke, brain tumors or injuries, including those that can occur in surgery, but in many cases the cause may not be known.
- Overflow incontinence occurs when your bladder remains full and leaks urine. You may feel as though you need to empty your bladder but cannot. Or you may urinate a small amount, but feel like your bladder is still full. Frequent or constant dribbling of urine also is a sign of this type of incontinence, which is rare in women. A damaged bladder or a blocked urethra can cause an inability to empty the bladder. Diabetes and other diseases can cause nerve damage that weakens the bladder muscle. Urinary stones or tumors also can block the urethra, which can force urine to remain in the bladder and even back up the urinary tract.
- Functional incontinence is untimely urination because of physical disability, external obstacles or problems in thinking or communicating that prevent a person from reaching a toilet. This may occur with severe arthritis, after joint replacement or with dementia such as seen in Alzheimer’s disease.
- Mixed incontinence is a combination of types of incontinence, usually stress and urge. In some studies, mixed incontinence is the predominant form of incontinence.
Diagnosis
If you’re suffering from incontinence (the inability to control urination), don’t be afraid to tell your health care professional what you’re experiencing. By talking with your health care professional, you can find out why you’re having bladder control and urinary leakage problems and what kind of treatment is best for you. Remember, incontinence isn’t a disease: it’s a signal of 1 or a lot of of a large vary of conditions. Make sure you tell your health care skilled what prescription and over-the-counter medications you’re taking, as several medication will contribute to incontinence.
To diagnose the reason behind your incontinence, your health care skilled can initial raise questions about your urinary habits and anamnesis. You should receive a thorough physical examination, including a pelvic exam, in which your health care professional will look for medical conditions that may be causing leakage, such as infections, tumors or impacted stool.
Constipation, or rare gut movements that pass tiny amounts of onerous, dry stool, can cause the stool to pack the intestine and rectum so tightly that the normal pushing action of the colon cannot move and discharge the stool. This condition, known as impacted stool or fecal impaction, occurs most often in the elderly or nursing home populations. It will manufacture incontinence because the packed bowel and body part swells and presses against the tract, obstruction flow of excretion. Loosening and removing the compact stool, typically by taking softening medication and having a health care skilled chop up and extract the stool with a finger inserted within the anus, relieves the urinary incontinence. Constipation ought to be avoided in any lady seeking to boost continence.
You may be asked to keep a diary of your urinary patterns for at least three days and up to a week. In the bladder diary, you record what, when and how much liquid you drink; how many times you urinate and how much; how many leaks you have; whether you felt Associate in Nursing urgency to urinate; and what you were doing at the time you older a leak.
Your health care skilled can also perform some tests, looking on the kind and suspected causes of your incontinence, including:
- Urinalysis, in which you will provide a sample of your urine that will be analyzed for the evidence of blood, infection, urinary stones and other abnormalities that can cause leakage.
- Cough check, in which you first relax and then cough while your health care professional looks for urine leakage. This take a look at checks for enuresis and should be performed either lying down or Associate in Nursing upright position.
- position.Post-void residual (PVR) activity take a look at that’s performed to envision what quantity excretion remains in your bladder once excretion. In this take a look at, you drink fluids and urinate into a measure pan. Then, your health care skilled drains the remaining excretion in your bladder for activity by inserting alittle, pliable tube, referred to as a tube, through the duct into the bladder. Alternatively, your health care skilled measures the excretion remaining within the bladder by mistreatment bladder ultrasound, in which a machine directs sound waves at the bladder and produces shadowy images from which the amount of urine in the bladder can be determined. Your health care skilled will justify what your PVR readings mean.
- Blood tests to ascertain levels of gear within the blood which may be associated with disorders or diseases which will cause incontinence.
If the results of the fundamental analysis and initial tests fail to purpose to a definitive identification, your health care skilled might refer you to a specialist, such as a urologist, who treats urinary tract disorders, or a urogynecologist, who treats urinary tract problems in women. Your health care skilled additionally might suggest the subsequent further tests:
- Urodynamic testing Urodynamic testing assesses bladder and sphincter function, including the pressure and volume of urine in the bladder and the pressure and flow of urine from the bladder through the urethra. One test, referred to as cystometry, measures contractions of the bladder muscle as it fills and empties by inserting a catheter through the urethra into the bladder and filling it with water. As part of the test, another tiny tube is inserted into the rectum or vagina to measure pressure on your bladder when you cough or exert pressure. Urodynamic testing additionally might embody imaging, such as X-rays or ultrasound, to examine changes in the position of the bladder and urethra during urination, coughing or straining.
- Cystoscopy, a test that uses a tiny telescope-like instrument that allows your health care professional to see inside the bladder and urinary tract and examine them for problems. You may be some native desensitising jelly and medicine to relax you before the take a look at, which involves inserting a thin tube that contains a miniature camera through the urethra and into the bladder.
Your health care skilled {may also|can also|may|may furtherly |might also|may additionally} perform additional tests to rule out girdle weakness because the reason behind your incontinence, including one called the Q-tip test. The Q-tip take a look at measures the distinction within the angle of the duct once it’s at rest versus once it’s straining. If the angle changes quite thirty degrees, there is most likely significant weakness in the pelvic floor muscles.
Be sure to debate together with your health care skilled that tests ar best for you, the exact procedures that will be followed when they are conducted and what the results mean in assessing your bladder management drawback Associate in Nursingd developing an acceptable course of treatment.
Treatment
The majority of incontinence conditions will be improved or cured with treatment, once the condition is delivered to the eye of a health care skilled and accurately diagnosed. Many women square measure too shamed or embarrassed to debate their incontinence condition with their health care team or suppose that treatment is not offered. In fact, a spread of treatment choices square measure offered for incontinence conditions, betting on which kind of incontinence is diagnosed: enuresis, enuresis, urinary incontinence or mixed incontinence.
Incontinence is not a disease, though it can be a symptom of an underlying condition, such as diabetes. However, most incontinence in girls is triggered by issues with the bladder and anatomical sphincter muscles, which may weaken with age and from accouchement.
Treatment options include:
- behavioral techniques
- pelvic muscle exercises
- medications
- Botox
- medical devices that block or capture urine
- electrical stimulation
- surgery
Your health care skilled will teach you ways that to manage your bladder and anatomical sphincter muscles. Behavioral techniques generally are tried first because once you learn them, you usually can do them yourself at home; they have no side effects; and they don’t preclude other treatment options. Types of behavioral techniques are:
- Pelvic muscle exercises, like exercising, strengthen the muscular parts of the epithelial duct closing mechanism and square measure typically employed in enuresis medical aid. Kegel exercises involve compressing the muscles, holding the force a couple of seconds, then restful, and continuance the method. The basic counseled program is to try and do 3 sets of eight to twelve contractions, holding every contraction for eight to ten seconds, performed a minimum of 3 to fourfold a week (preferably every day) for 15 to 20 weeks. The keys to success with girdle muscle exercises square measure accuracy (making positive you exercise the proper muscles) and compliance (sticking with the exercise program). Your health care skilled will assist you learn to spot the muscles. Sometimes training program and electrical stimulation square measure wont to improve exercise results.
- Biofeedback may be a coaching technique that teaches you ways to manage physical responses, like respiration, muscle tension, heart rate and blood pressure that are not normally controlled voluntarily. Biofeedback techniques may help you to gain control over your bladder and pelvic muscles and to strengthen the sphincter muscle. A display is placed on the muscles that permit you recognize after you have shrunk them, and how strong the contraction was. In one study of 222 girls with enuresis, behavioural coaching combined with training program LED to a sixty three % reduction in incontinence. Over the years, thought health care professionals and insurers have more and more accepted training program techniques.
- Electrical stimulation stimulation involves using brief doses of electrical stimulation to strengthen muscles in the lower pelvis in a way similar to exercising the muscles. It may embrace use of devices like a radiofrequency treatment (Renessa) or girdle floor training program. Electrodes square measure quickly placed within the epithelial duct or body part to stimulate close muscles. This procedure will stabilize overactive muscles and stimulate contraction of urethral muscles. Electrical stimulation will be wont to scale back each enuresis and enuresis, though it is rarely used for primary stress incontinence. Some insurers might not buy this procedure, so be sure to check on your coverage.
- Bladder coaching is is employed to treat enuresis, but may also be used for other types of incontinence. Your health care provider teaches different ways to control the urge to urinate, such as through distraction (thinking about things other than having to go to the bathroom), taking a deep breath, contracting the pelvic muscles, or visualizing the urge as a wave that rises and falls. You also follow a elimination schedule that gently lengthens the time between lavatory visits.
Several medications is wont to treat incontinence and area unit typically utilized in conjunction with behavioural techniques. Because several medicine will have facet effects, will move with alternative medications, or shouldn’t be employed by folks with bound medical conditions, solely you and your health care professional can determine which medications are right for you.
Some of the medications area unit medicine that block production and use of a chemical that prompts bladder contractions. These medications area unit typically wont to treat urinary incontinence, however they ought to not be taken by if you’ve got retentiveness, bound sorts of abdomen issues, or narrow-angle eye disease. Here area unit a number of the foremost common medicine for active bladder/urge incontinence.
- Oxybutynin blocks bladder muscle contractions and is suggested for treatment of urinary incontinence. Oxybutynin is available in tablets (Ditropan), extended-release tablets (Ditropan XL), patch (Oxytrol) and gel form (Gelnique). The patch kind recently was approved because the 1st over-the-counter treatment for active bladder in ladies (Oxytrol for Women). It became offered over-the-counter in fall 2013 for girls however can stay offered by prescription just for men. The patch is applied every four days. The prescription gel is applied daily. Common facet effects of oxybutynin embody mouth, nose and throat dryness; headache; constipation; nausea; lightheadedness and blurred vision. The patch and gel may cause skin irritation.
- Tolterodine tablets (Detrol) is a drug for overactive bladder. Side effects embody cause xerotes, headaches, constipation, blurring of near vision, dizziness, upset stomach and abdominal pain.
- Trospium (Sanctura). This drug is approved for the treatment of overactive bladder. Side effects include dry mouth and constipation.
- Solifenacin (Vesicare) and darifenacin (Enablex). These drugs are also approved for the treatment of overactive bladder. Side effects include constipation and dry mouth.
- Imipramine (Tofranil). This is an antidepressant drug that may occasionally be prescribed together with other medications to treat incontinence. It works by causing the bladder muscle to relax while simultaneously causing the smooth muscles at the neck of the bladder to contract. Side effects include blurred vision, dizziness, dry mouth, fatigue, insomnia and nausea.
- Fesoterodine (Toviaz). This pill is approved to treat active bladder with symptoms of urinary frequency, incontinence and urgency. It works by reducing spasms of the bladder muscles. Side effects might embody hypersensitivity, blurred vision, dizziness, constipation, upset stomach, insomnia and dry mouth, eyes or throat.
- Mirabegron (Myrbetriq). Mirabegron is the first beta-3 adrenergic agonist to be approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for incontinence caused by active bladder (OAB). It is a once-a-day pill that works by relaxing the bladder’s detrusor muscle to regulate the filling and storage of urine. This will increase bladder capability and helps management the frequent urge to urinate, as well as urine leakage. Mirabegron will cause some facet effects, including headache, high blood pressure, urinary infection and upper respiratory infection.
If you have mild to moderate stress incontinence, your health care professional may prescribe one or more of the following medications, however, no drugs have been proven effective for treating stress incontinence:
- Anticholinergic medicine which can assist with mixed incontinence, such as oxybutynin (Ditropan, Oxytrol), tolterodine (Detrol), darifenacin (Enablex), trospium (Sanctura) or solifenacin (Vesicare)
- Alpha-adrenergic agonist medicine, such as phenylpropanolamine and pseudoephedrine, which can strengthen the sphincter and work to improve symptoms in many people. These drugs are rarely prescribed, however, because of their potential side effects on the heart.
- The tricyclic antidepressant imipramine (Imipramil, Tofranil), which works similarly to alpha-adrenergic drugs.
Absorbent products may be used while treatments are under way or as part of a treatment plan, in combination with behavioral training, exercises, medications or other treatment options.
Surgery
Surgical procedures conjointly might facilitate ladies with urinary incontinence once less invasive therapies don’t improve symptoms. Surgery could be a serious step that has to be mentioned along with your health care skilled thus you clearly perceive all the risks, likewise because the possibilities that the surgery will relieve your urine control and urinary tract support problems. Although the procedures do have high success rates, complications can occur, including recurrence of incontinence.
The most popular procedure in the United States and Europe today involves a mid-urethral polypropylene sling. A MD uses the artificial material to form a sling that compresses all-time low of the bladder and therefore the prime of the duct, preventing urine leaks. Alternatively, the surgeon may use a piece of pelvic connective tissue to create a sling.
Surgery may also involve bladder neck suspension. Done through associate abdominal incision mistreatment general or spinal, this surgical procedure provides support to the urethra and bladder neck, an area of thickened muscle where the bladder and urethra connect.
There ar several extra surgical procedures for urinary incontinence in ladies, and new techniques continue to emerge. Some techniques use many tiny incisions for insertion of instruments and a endoscope, a telescope that lets the surgeon see inside the abdomen and perform the procedure to raise the bladder or bladder neck or to get rid of urinary obstructions. Recovery from laparoscopic procedures could also be quicker and fewer painful than from open abdominal surgery, however like any surgery, there ar risks.
In very rare instances of complex stress incontinence, an artificial sphincter may be surgically implanted. A hollow, ringed device that encircles the duct is placed and full of fluid that squeezes the duct shut. A valve is deep-rooted beneath the skin that, when pressed, deflates the device, permitting urination. This procedure is particularly helpful for men who have weakened urinary sphincters as a result of treatment of prostate cancer; it is rarely used in women with stress incontinence.
Surgery to get rid of tissue-causing blockage within the tract or to enlarge alittle bladder may treat enuresis.
Other treatments for incontinence include:
- A pessary is a device inserted by a health care professional into the vagina to support pelvic organs. It either presses against or supports the vagina wall and the urethra, leading to less urine leakage in stress incontinence. It has to be removed, cleaned and reinserted regularly to prevent possible urinary tract infections and vaginal ulcers. There ar totally different forms of pessaries, and you’ll ought to strive many to get an honest match. Some patients could also be ready to take away and clean the prophylactic device by themselves.
- Catheters could also be used either perpetually or sometimes for enuresis not caused by a blockage, or in women who cannot empty their bladders because of muscle weakness, previous surgery or spinal cord injury. Your health care skilled will teach you the way to insert the tube through the duct into the bladder yourself thus you’ll drain weewee. If you employ a tube semipermanent, the tube will be connected to a urine collection bag that you can wear on your leg underneath clothing. You also need to be on the alert for urinary tract infections, which are possible with long-term catheter usage.
- Percutaneous leg bone nerve stimulation (PTNS) is associate possibility for girls with enuresis UN agency don’t answer life style changes or medications, as well as for those who don’t want to or cannot have surgery. The procedure involves delivering electrical stimulation to the sacral nerve that controls the bladder via the tibial nerve in the ankle that leads to nerves that control the pelvic floor.
- Sacral nerve stimulation is an electronic stimulation therapy that involves a surgically implanted sacral nerve stimulator resembling a pacemaker. More invasive than PTNS, it involves sending small, electrical impulses directly to the sacral nerve. The continuous electrical stimulation reduces or eliminates urgency, frequency and enuresis.
- Botulinum toxin type A (Botox) was recently approved by the FDA to treat women with incontinence from overactive bladder who have not responded to medications, as well incontinence in people with neurological conditions, such as multiple sclerosis or spinal cord injuries. Botox works to regulate incontinence by reposeful the bladder, increasing storage capability and reduces outpouring. Possible side effects may include urinary tract infections, painful or difficult urination and urinary retention.
- The use of radiofrequency energy to heat tissue within the lower tract may facilitate improve symptoms of incontinence. When the tissue heals, it is usually stronger and firmer, which can reduce urinary leaks.
Prevention
Although there’s no scientifically tried regime to forestall incontinency, maintaining your general health is often an honest step to move off sicknesses and malady which may cause incontinence. Healthy eating and weight control may be preventive measures, as there have been links between obesity and incontinence. Indeed, even modest weight loss has been incontestible to dramatically improve incontinence symptoms. Activities that exert pressure on pelvic muscles should be avoided, such as straining during bowel movements or heavy lifting. Persistent coughing from smoking can also stress girdle muscles, giving smokers one more reason to quit.
Performing girdle muscle, or Kegel, exercises, particularly throughout and once maternity, and using topical forms of estrogen may play a role in possibly preventing or treating incontinence. Your health care skilled will advise whether or not such therapies ar applicable for you.
Reducing alkaloid and alcohol consumption will improve the body’s ability to retain pee. Both substances can inhibit production of a hormone that concentrates and decreases the volume of urine by increasing reabsorption of fluid by the kidneys.
Your health care provider may suggest you keep a chart to track your urinary frequency to help determine whether your fluid intake is reasonable. Emptying your bladder four to eight times in 24 hours is normal, as is urinating about every three to four hours during the day, as well as getting up once at night to go to the bathroom.
Although there’s no specific diet to forestall incontinence, it is thought certain foods and drinks can irritate the bladder and should be avoided if consuming them appears to produce or increase symptoms:
- carbonated beverages
- coffee or tea, including decaffeinated forms
- yogurt
- citrus juice and fruits
- tomatoes and tomato-based products
- bananas
- artificial sweeteners
- chocolate
- spicy foods
- vinegar
- processed meats and fish
Some medications may contribute to incontinence. Talk with your health care professional if you experience urinary leakage while taking these drugs:
- diuretics, or “water pills,” that increase urine flow, including bumetanide (Bumex), forosemide (Lasix), and theophylline (Bronkodyl)
- sedatives and sleep aids, including diazepam (Valium), flurazepam (Dalmane) and lorazepam (Ativan)
- antihistamines and cold and allergy medications, such as benztropine (Cogentin)
- antidepressants and antipsychotics, including amitriptyline (Elavil), desipramine (Norpramin) and haloperidol (Haldol)
- angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, which are often prescribed for high blood pressure and congestive heart failure, including benazepril (Lotensin) and captopril (Capoten)
Facts to Know
- Millions of Americans suffer from incontinence, and plenty of of them square measure ladies.
- Although incontinence is most rife among older ladies, it will occur at any age and in each genders.
- Many women with incontinence ne’er discuss it with their health care professionals. In most cases, treatment will improve or cure incontinence, once the condition is delivered to the eye to a health care skilled.
- Incontinence is a symptom, not a disease. It has a variety of causes. Urine leakage can be caused by problems that, when treated, stop the incontinence, including urinary tract infections, bladder irritations and constipation.
- Stress incontinence is that the most typical style of incontinence among younger ladies. It consists of piss outflow once any physical pressure is placed on the bladder, like reflex, coughing or effort. Another common sort of piss management drawback in ladies is enuresis, characterised by a explosive, robust urge to urinate however associate degree inability to create it to the rest room in time. It will be caused by a disorder referred to as “overactive bladder.” ladies will have a mix of those issues, referred to as mixed incontinence.
- Overflow incontinence, that is that the feeling that the bladder is often full, among dribble of piss, is rare in women. It will be caused by polygenic disease, all medical specialty diseases or associate degree obstruction within the tract which will result in serious health problem, so if you experience such symptoms, see your health care professional.
- With treatment, incontinence can be improved or cured in many cases. Treatment depends on the kind of incontinence and its causes. Therapy choices embrace straightforward behavior therapy techniques ladies will learn to try to to themselves, medications, Botox injections, use of special devices and surgery. Talk together with your health care skilled regarding what treatments could assist you.
- Behavior modification techniques are often the first-line treatment for incontinence, but their success depends on your ability to stick to with them. Pelvic muscle exercises, such as Kegel exercises, strengthen weak muscles that support the urinary system. Studies show that when done correctly, Kegel exercises can be effective in helping to prevent stress incontinence. Bladder training may also change urination habits.
- There square measure varied surgical techniques for treating enuresis, and many of them have been highly successful. Some procedures square measure minimally invasive and may have fast recovery times. But surgery does carry risks and needs to be fully discussed with your health care professional before you choose it as a treatment option.
- Absorbent pads and adult diapers are generally recommended by health care professionals for use while undergoing other treatments or for long-term use in conjunction with other treatments—not as the only option available.
- Isn’t incontinence just part of the aging process?No, incontinence, or the lack to manage excretion, will occur at any age. Because urinary incontinence is most common in the elderly, and it is a major cause of admission to nursing homes, it is often mistakenly thought of as a problem suffered only by older people.
- Why do I need to see a health care professional about urine leakage when I can just wear a pad??Incontinence is not normal. It is a proof which will have several causes. Some of those causes can be problems that are easily treated to stop the incontinence, such as urinary tract infections, bladder irritations and constipation. Other causes are often additional serious, such as an obstruction in the urinary tract, which can cause urine to back up and harm the kidneys. The most common causes are weak pelvic muscles that support the urinary tract and an overactive bladder, both of which can be treated or improved in most cases. If you do not seek advice from your health care skilled, your problem could persist and even worsen. Continual exposure to urine can result in skin rashes and infections. There’s no ought to suffer with this downside once there square measure several treatment choices which will improve it, or even cure it.
- What kinds of treatments are there for incontinence?There are many kinds of therapies for incontinence, depending on the type you have and the cause of your problem. Initial treatment could embody girdle muscle exercises or dynamic your excretion patterns or habits. Several medications square measure obtainable that will facilitate and should be employed in conjunction with girdle muscle exercises and bladder coaching techniques. Insertable devices and bulking agent injections also may relieve urinary leakage. Additionally, there are several surgical techniques that can be highly successful. Ask your health care skilled concerning the risks and edges of every possibility, and what course of medical aid may best assist you.
- I hear a lot of talk about overactive bladder. What’s the difference between it and incontinence?An overactive bladder can cause urge incontinence. When your bladder muscles contract to expel urine when you don’t want them to do so, you have an overactive bladder. Frequent visits to the bathroom; unforeseen, overwhelming urges to urinate; ANd AN inability to induce to a bathroom in time square measure characteristics of enuresis caused by an hyperactive bladder.
- Must I have surgery to stop my urine leakage?Not necessarily. Surgery are often extremely booming in several cases of incontinence, especially those caused by weak pelvic muscles that allow the bladder to drop onto its neck and prevent the urinary sphincter muscle muscles from staying tight stressed, causing leaks. But having AN operation isn’t the sole treatment obtainable. Talk to your health care skilled concerning what treatments square measure best for you.
- Will I have incontinence when I reach menopause?There is no way to predict who will become incontinent. It is true, however, that a lot of biological time and biological time ladies have enuresis. Weak girdle muscles that support the bladder and duct could cause enuresis. Decreases in levels of the endocrine oestrogen even have been related to less muscular pressure round the duct, reduced urinary sphincter strength, thinning of the lining of the urethra and reduced bladder support.
- What can I do to prevent incontinence?There is no scientifically established plan to stop incontinence. However, maintaining smart overall health, particularly with regards to weight, is always a good idea. And, since weak girdle muscles square measure at the basis of the many body waste management issues, exercising them may help maintain bladder control, especially during and after pregnancy. Your health care skilled will tell you whether or not girdle exercises square measure right for you and teach you the way to try and do them properly. Reducing alkaloid and alcohol consumption will improve the body’s ability to retain body waste. Also, some foods and beverages may irritate the bladder and should be avoided if you’re having urinary control problems. Some prescription and over-the-counter medications will cause incontinence, too. If you are experiencing incontinence, talk with your health care professional about it.
ause incontinence, too. If you’re experiencing incontinence, talk with your health care professional about it. - My doctor wants me to have an urodynamic test. What is it, and will it hurt?This type of testing assesses bladder and sphincter function, including the pressure and volume of urine in the bladder, and the pressure and flow of urine from the bladder through the urethra. One test, referred to as cystometry, measures contractions of the bladder muscle as it fills and empties by inserting a catheter through the urethra into the bladder and filling it with water. Another tiny tube is inserted into the rectum or vagina to measure pressure on your bladder when you cough or exert pressure. Urodynamic testing conjointly could embody imaging, like X-ray or ultrasound, to look at changes within the position of the bladder and duct throughout excretion, coughing or straining. The use of catheters can be uncomfortable but these tests are well-tolerated. Imaging tests are generally noninvasive and do not hurt.



