Treatment of vascular disease?
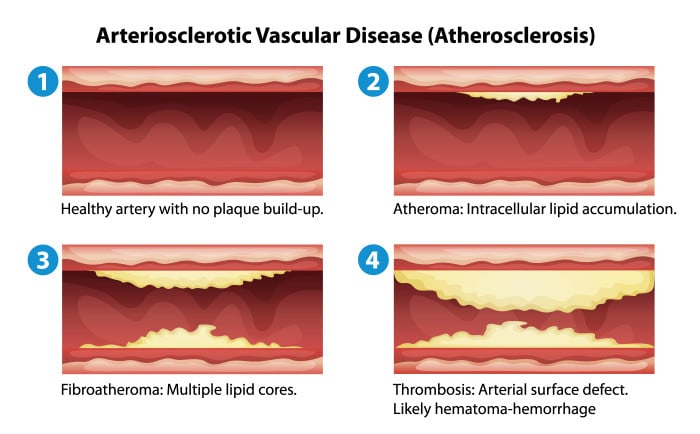
The most common risk factor for coronary heart disease and heart attack is vascular disease. This type of condition also causes stroke as it is affecting the arteries in the neck. The two most common types of vascular disease include peripheral arterial disease or PAD and the peripheral vascular disease or PVD. PAD is a circulatory condition in which there is a narrowing of the peripheral arteries to the patient’s stomach, legs, head, and arms. These affected areas don’t receive the proper amount of blood flow to keep up with demand. On the other hand, peripheral vascular disease is the class of diseases of blood vessels outside the heart and brain. This condition happens when there is a narrowing of vessels, responsible for carrying blood to the arms, stomach or kidneys, and legs.
The treatment for vascular disease will be based on your signs and symptoms, the results of physical exams and tests, and risk factors. The overall goals of treating this condition are as follow:
to reduce the chance of coronary failure and stroke
to reduce symptoms of claudication
to improve mobility
to improve overall quality of life
to prevent complications
Depending on the situation, treatment may stop or slow down the progression of the disease and reduce any risks of complications. Without treatment, vascular disease may progress, resulting to serious tissue damage in the form of gangrene (tissue death) or sores due to insufficient blood flow. Extreme cases of vascular diseases are also referred to as critical limb ischemia (CLI) or the amputation of part of the leg or foot that is affected by the disease.
Physical Activity
Routine physical activity can improve vascular disease symptoms and lower the risk factors for high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, including LDL cholesterol, and excess weight. Doing regular exercise can improve the distances that you can comfortably walk. Ask your doctor about your interest and need in undergoing a supervised exercise program. If a supervised program is not suitable for you, ask your doctor to help you develop a customized exercise plan. Most of the exercise programs begin slowly, including simple walking. As your condition improves, you will build up the amount of time you can walk before developing pain. Once your vascular disease symptoms become better, try to be more active and do other exercises.
Stop Smoking
Smoking does not do our body any good and it even raises the risk for P.A.D. Cigarette smoking increases the risk for other diseases, like coronary heart disease and heart attack. It also worsens other coronary heart disease risk factors. If you’re having a hard time quitting, talk to your doctor about programs or products that can help you stop this habit. There are hospitals, workplaces, as well as community groups that offer classes to help people quit smoking. You might also want to avoid secondhand smoke.
Healthy Eating
Together with the lifestyle changes above, your doctor may advice you to start eating heart-healthy food. This is to treat atherosclerosis or the most common cause of P.A.D. Having a heart-healthy diet can help control blood pressure and even cholesterol levels.
If these solutions do not work, medications and surgical procedures may also be advised. If you want to know more about treatment options for vascular diseases, don’t hesitate to get in touch with Vascular and Interventional Centre. Trust their knowledgeable staff to help you understand, cure, and manage vascular diseases. Head over to their website for any questions you have or to schedule a personalized appointment today.



